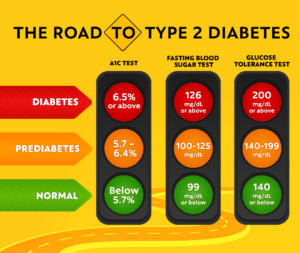
“From Prediabetes to Wellness: Your Journey to Stop Diabetes”
To reduce the risk of developing Prediabetes and prevent its progression to Type 2 Diabetes, implementing healthy lifestyle changes is crucial. Here are some measures you can take:
- Manage Your Weight: Excessive weight gain is a significant risk factor for diabetes. Losing just 5% of your body weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: A healthy and balanced diet plays a pivotal role in reducing the risk of diabetes. Consider the following dietary choices:
Choose foods with a low glycemic index to help control blood sugar levels.
Include high-fiber foods in your diet, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
Limit your intake of carbohydrates, especially refined carbohydrates like sugary snacks, white bread, and sugary cereals. These can have detrimental effects on blood sugar.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity is essential in preventing diabetes. Try to incorporate the following into your routine:
Engage in regular exercise, such as walking, jogging, or cycling.
Take leisurely walks in the park to increase your physical activity.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
By following these healthy lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce the risk of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes.