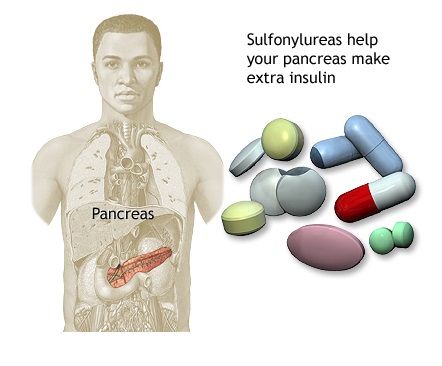
The possibility of reacting to sulfonylureas increases if you have a history of allergy to sulfa-based antibiotics (accounting for about 10%). Patients who have had adverse reactions to sulfa-based antibiotics may wish to steer clear of non-antibiotic sulfonamides. The first dosage’s administration necessitates medical supervision.
The choice of diabetes medication, including whether to use sulfonylureas, depends on various factors, including the individual’s specific medical history, glucose control goals, and any contraindications or side effects they may experience.
By combining sulfonylureas with a healthy lifestyle, the risk of developing diabetes complications can be considerably reduced.
Common brands of Sulfonylureas in Pakistan includes:
- Amaryl® (glimepiride) and Amaryl M® (glimepiride + metformin)
- DAONIL® (gilbenclamide)
- Neodipar® (Metformin)
- G-Helix (Glimepiride 1mg,2mg,3mg,4mg)
Meglinitinide/ Phenylalanine analogues
Meglitinides are another class of medications used to manage type 2 diabetes. These drugs work by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, similar to sulfonylureas, by selectively binding to a receptor distinct from sulphonylureas (SUR1/KIR 6.2) and inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels. But they have a shorter duration of action. This means that they cause a rapid increase in insulin secretion, which is especially helpful for controlling blood sugar levels after meals. Here are some key points about meglitinides:
- Mechanism of Action: Meglitinides, like repaglinide and nateglinide, stimulate the release of insulin from the beta cells in the pancreas by binding to the same receptors as sulfonylureas. However, meglitinides have a faster onset and shorter duration of action.
- Indications: Meglitinides are used to treat type 2 diabetes, typically in individuals whose blood sugar levels are not adequately controlled through lifestyle modifications (such as diet and exercise) alone. They are often prescribed in combination with other diabetes
- Administration: Meglitinides are usually taken orally before each meal to help control post-meal blood sugar spikes. The dose is typically adjusted based on the timing and size of meals.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of meglitinides include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain, and gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea. Due to their shorter duration of action, meglitinides are less likely to cause prolonged periods of low blood sugar compared to sulfonylureas.
- Precautions: These medications should be used with caution in individuals with impaired liver function and are generally not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Timing: Unlike sulfonylureas, meglitinides are taken shortly before meals to stimulate insulin release in response to the meal. This can help control post-meal glucose levels.
- Combination Therapy: Meglitinides are often used in combination with other diabetes medications, such as metformin or other oral antidiabetic drugs, to achieve better blood sugar control.
- Individualization: The timing of meglitinide doses and the dosage itself are often individualized to match a person’s meal schedule and specific blood sugar patterns.
Commonly used Megitinide/ Phenylalanine analogue are:
- NOVONORM (Repaginate 0.5mg,1mg,2mg)
- Limzil (Repaglinide 2mg)