What is Diabetes Type 2 remission
Diabetes type 2, a prevalent chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, has long been considered a progressive and lifelong ailment. However, recent medical research and advancements have revealed a promising concept: diabetes type 2 remission. This phenomenon signifies a substantial improvement in blood glucose control to the extent that medication may no longer be required, and the individual’s health profile resembles that of a non-diabetic individual. In this article, we explore the concept of diabetes type 2 remission, its methods, and its implications.
Understanding Diabetes Type 2 Remission
Diabetes type 2 is primarily characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, this condition can progress, necessitating medication and sometimes insulin injections to manage glucose levels effectively.
Diabetes type 2 remission, however, challenges the notion that the condition is irreversible. It refers to a state where blood glucose levels return to normal or near-normal levels without the need for ongoing medication. Achieving remission signifies a significant improvement in the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, often associated with weight loss, improved lifestyle choices, and other interventions.
Methods of Achieving Diabetes Type 2 Remission
- Lifestyle Changes: One of the most potent strategies for achieving diabetes type 2 remission is through substantial lifestyle modifications. These include adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and losing weight. A combination of a balanced diet rich in whole foods, reduced intake of processed sugars and refined carbohydrates, and regular exercise can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
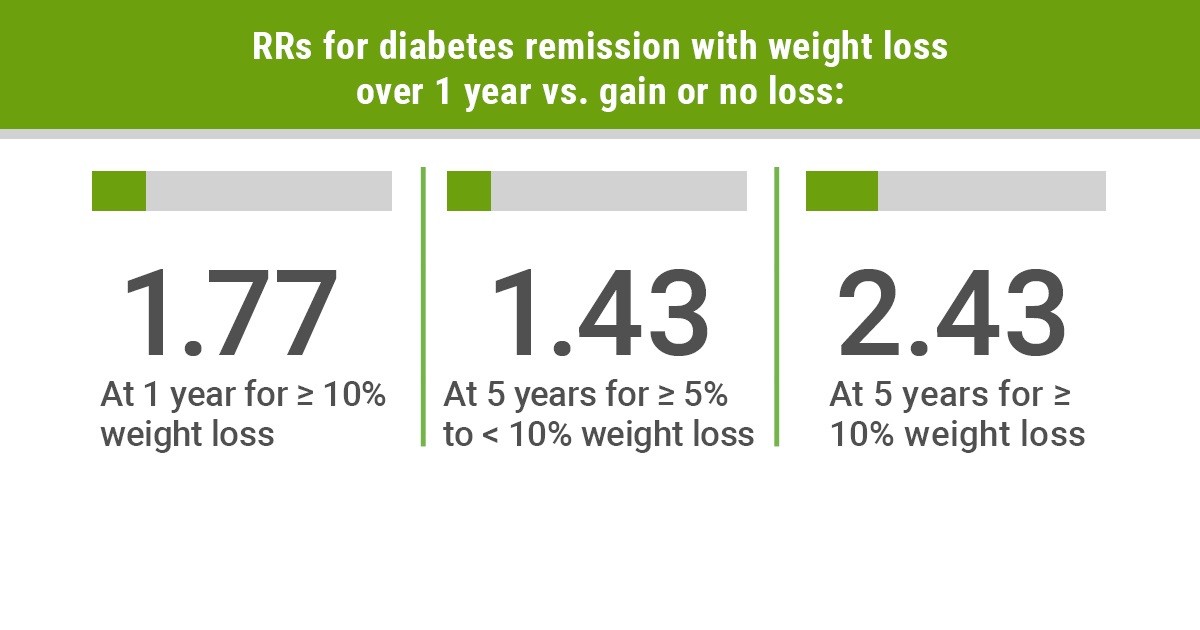
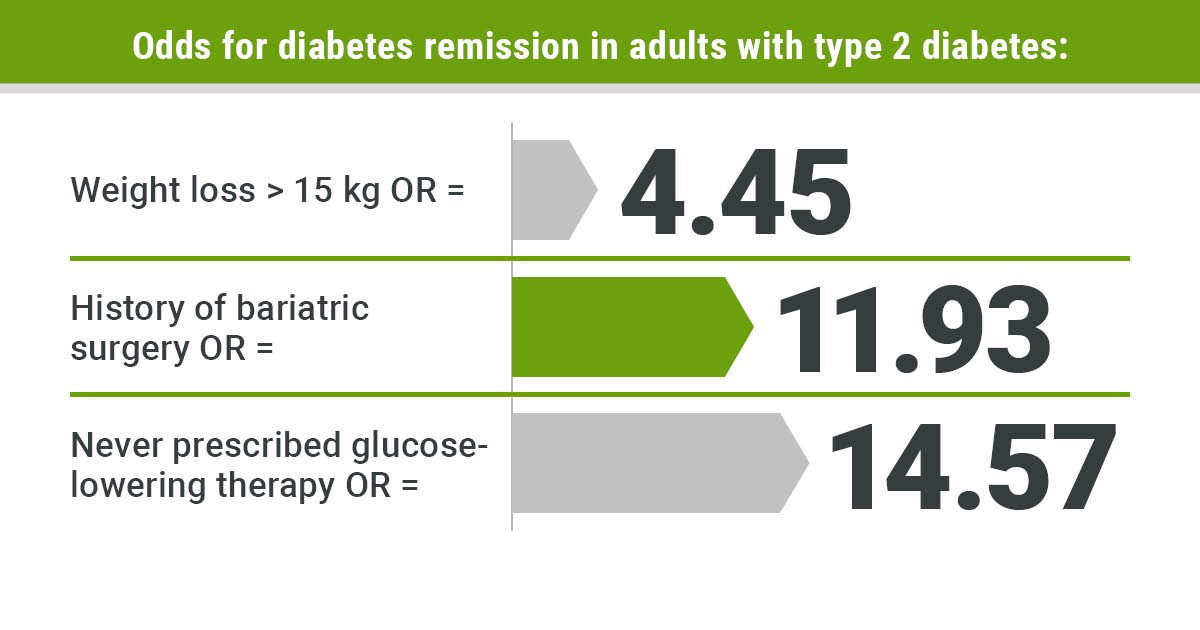
- Weight Loss: Excess body weight, especially abdominal fat, is strongly linked to insulin resistance and diabetes. Shedding extra pounds through a combination of diet and exercise can lead to improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation. Some individuals have achieved diabetes remission solely through weight loss.
- Bariatric Surgery: For individuals with severe obesity and diabetes, bariatric surgery may be considered. Procedures like gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy not only aid in significant weight loss but also often lead to remarkable improvements in blood sugar control. In some cases, diabetes remission occurs shortly after surgery.
Implications and Considerations
Achieving diabetes type 2 remission is an encouraging prospect that can lead to various health benefits, including reduced risk of diabetic complications like heart disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage. However, it’s essential to note that remission doesn’t equate to a complete cure. Sustaining remission requires ongoing commitment to healthy lifestyle choices and monitoring blood sugar levels