- Meal Timing and Frequency:
-
- Aim for regular meal times spaced throughout the day to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Consider eating three main meals and 1-2 small, balanced snacks as needed.
- Carbohydrate Counting:
- Learn about carbohydrate counting to help manage blood sugar levels. Consult a registered dietitian to guide you through this process.
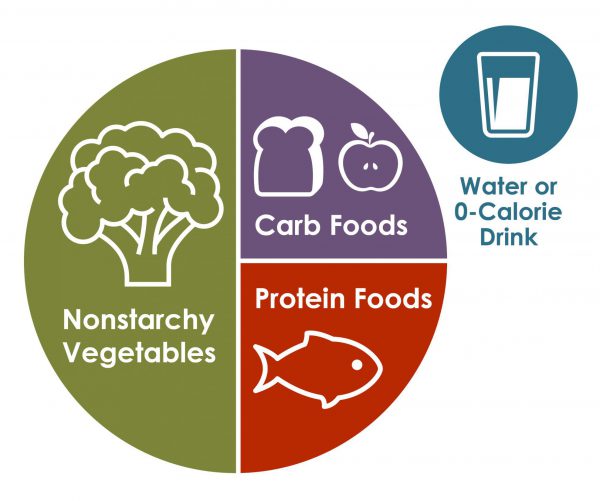
- Monitor portion sizes of carbohydrate-containing foods, as they have the most direct impact on blood sugar.
- Glycemic Index (GI):
- Familiarize yourself with the glycemic index of foods. Lower GI foods cause slower and more gradual increases in blood sugar.
- Focus on incorporating more low-GI foods into your diet, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
- Fiber Intake:
- Aim for an adequate intake of dietary fiber, as it can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve digestive health.
- Include whole grains, vegetables, fruits, legumes, and nuts in your diet to boost fiber intake.
- Protein Balance:
- Include a source of lean protein in each meal to help control hunger and stabilize blood sugar.
- Choose lean meats, poultry, fish, tofu, legumes, and low-fat dairy products.
- Healthy Snacking:
- Opt for nutrient-rich snacks that contain a mix of protein, healthy fats, and fiber to prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar.
- Examples include a small handful of nuts, Greek yogurt with berries, or vegetable sticks with hummus.
- Portion Control:
- Use measuring tools to gauge portion sizes, especially when you’re starting to manage your diet.
- Be mindful of your overall calorie intake to achieve or maintain a healthy weight.
- Label Reading:
- Read nutrition labels to identify the carbohydrate content and serving sizes of packaged foods.
- Pay attention to added sugars and opt for products with minimal processing.
- Fluid Intake:
- Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limit sugary beverages, caffeine, and alcohol, as they can affect blood sugar levels.
- Cooking Methods:
- Choose healthier cooking methods like baking, grilling, steaming, or sautéing instead of frying.
- Use herbs, spices, and citrus juices to flavor foods instead of excessive salt or sugary sauces.
- Meal Diversity:
- Plan a variety of foods to ensure you’re getting a wide range of nutrients.
- Incorporate different colors of fruits and vegetables to ensure a mix of vitamins and antioxidants.
- Managing Stress:
- Practice stress-reducing techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing, as stress can impact blood sugar levels.
- Individualization:
- Work with a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes management to create a personalized meal plan based on your unique needs, preferences, and goals.
- Monitoring and Adjustments:
- Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels and keep a record of your meals, snacks, and medications. Adjust your diet as needed in consultation with your healthcare team.
Diabetes care demands a sustained effort over time, with a balanced diet playing only a small role. Proper exercise routine, efficient medication administration, and regular consultations with your healthcare professional form fundamental aspects of successful diabetes management.