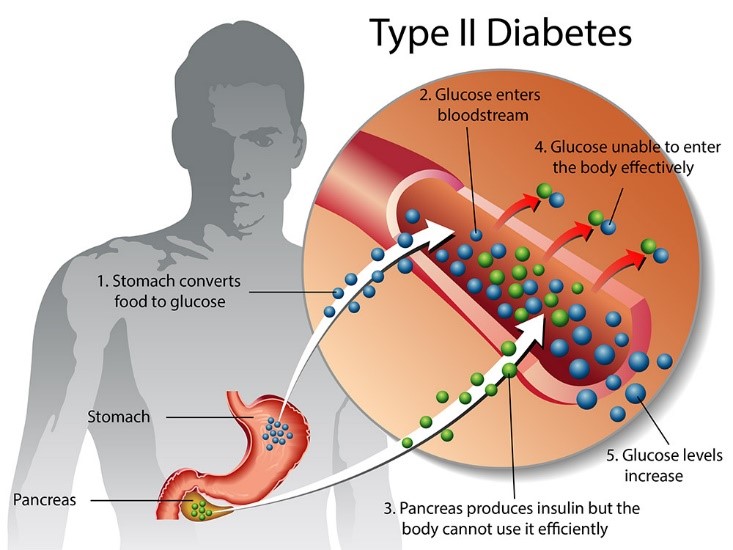
Type 2 diabetes is indeed the most common form of diabetes, and it is characterized by high blood sugar levels. This condition occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or when the insulin it produces doesn’t work effectively, a condition known as Insulin Resistance. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing cells to take in glucose for energy.
Management and treatment of type 2 diabetes typically involve a combination of lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medications.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating a balanced diet and increasing physical activity are essential for managing type 2 diabetes. A well-balanced diet should include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Regular physical activity helps the body use insulin more effectively and can improve blood sugar control.
- Medications: In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to control blood sugar levels. Medications may be prescribed to help lower blood sugar.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for people with type 2 diabetes. This helps in understanding how diet, exercise, and medications are affecting blood sugar and allows for adjustments as needed.
- Complications: Uncontrolled type 2 diabetes can lead to various complications, including heart disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, and eye issues.
- Risk Factors: Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include family history, being overweight or obese, a sedentary lifestyle, and certain ethnic backgrounds.
- Remission: Some people with type 2 diabetes can achieve remission by making significant lifestyle changes, particularly by losing a substantial amount of weight. Remission doesn’t mean a cure; it means that blood sugar levels are well-controlled without the need for medications.